Place Pulse
MIT Media Lab study looks to effect urban development through Google Street View-powered surveys


Remember the feeling the first time walking down a desolate street in a foreign city or waiting on the corner in a new neighborhood to meet a friend? We all constantly judge our surroundings, whether knowingly or subconsciously; our ability to determine our level of safety, advantage or opportunity from our perceived situation is an essential evolutionary tool for survival. While usually these judgements happen on minute levels, a new project from the MIT Media Lab seeks to tap the power of the information within these determinations on a large, collective scale.

The crowd-sourced urban survey, Place Pulse, is run by Phil Salesses, Anthony Devincenzi and Cesar Hidalgo, all of the MIT Media Lab, and Mauro Martino of Northeastern University Center for Complex Network Research. This team of technologists, researchers, designers and artists use the work of Kevin Lynch from the 1960s as a jumping off point for understanding urban perception, taking advantage of today’s tools to expose large test groups to urban imagery.

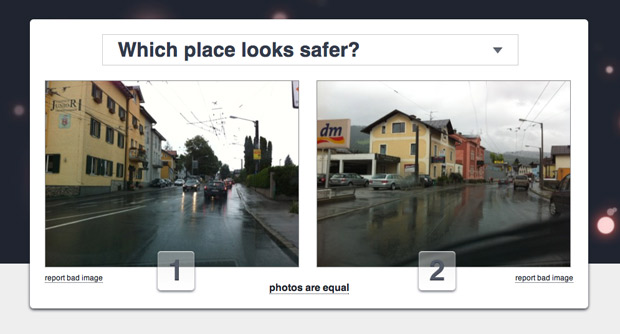
With a goal of improving an urban population’s overall happiness by understanding how people perceive certain areas, the surveys present participants with two side-by-side images and three topical questions—”Which place looks more unique?”; “Which place looks more upper class?; and “Which place looks safer?” The source images come from Google Street View, and surveys are created and taken by a willing community of participants. Capitalizing on geolocation services and social networks creates easily-visualizable data on a near global scale.
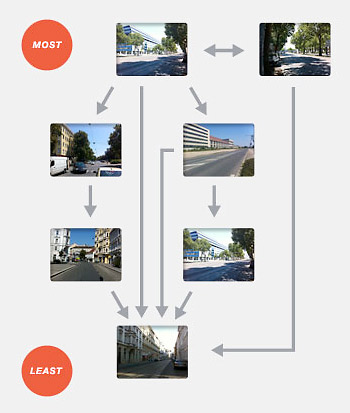
The data produced determines which urban features create certain perceptions. Laying the answers to these questions into graphs and combining them with the graphs of other participants makes up what the researchers call a “perception network.” This network of data can then be analyzed to make assumptions about general perception of certain areas, assisting in forming hypotheses about urban planning and development.
While still in the very early stages, the project presents a fascinating way to use what have become everyday technologies to conduct massive social experiments. The resulting dataset has the potential to impact city design and to assist local governments in targeting problem areas to improve inhabitant happiness. The more people who participate, the greater the success, so head over to the project and take the survey. Final results will be available 14 August 2011.









